Explore the API using Postman#
To discover the API interactively, using Postman is recommended:
Note
The Chrome-Extension version of Postman is deprecated and it is recommended to use the native app available instead.
Configuration#
To easily follow links returned by request based on the API,
go to the menu under the wrench icon on the top right
choose Settings
activate the option Retain headers on clicking on links by selecting ON:
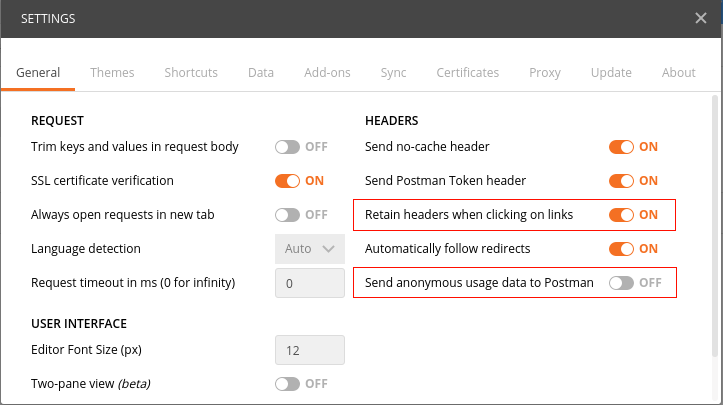
This option makes sure, once a HTTP-Header is configured, that it will be reused during subsequent requests, provided these are initiated by clicking on links resulting from the initial request. This way navigating the structure using the API becomes a snap.
The option Send anonymous usage data to Postman should be deactivated by setting to OFF.
Usage#
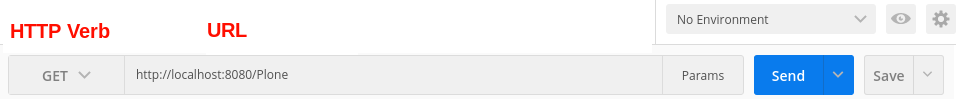
Choose the suitable HTTP Verb to be used for your request. This can be selected using the Postman drop-down menu.
Enter the Object URL of the object that should be the target of a request into the URL field right to the HTTP Verb:
Now set the appropriate HTTP headers.
the Authorization Header for the authentication related to the right user
the Accept Header to initiate the right behaviour by the API related to this Request.
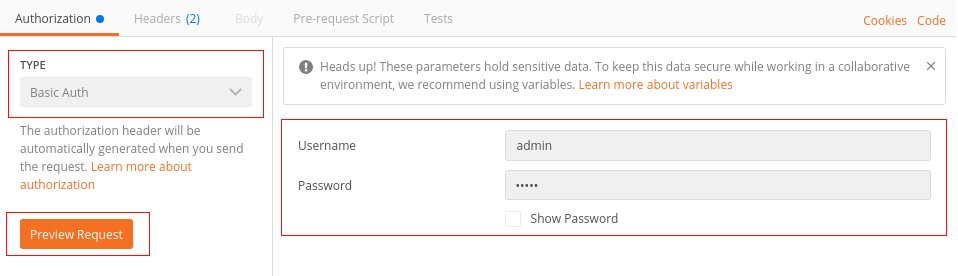
To set the Authorization Header, there is a reserved tab that is responsible to generate the final Header based on the authentication method with username and password.
You have to select:
in the drop-down menu the term Basic Auth as the authentication method, and
a valid existing user with appropriate permissions.
After providing these parameters you can create the resulting Authorization Header and insert it into the prepared request by clicking on Preview Request.
Under the Headers tab, you now need to insert in the Accept Header application/json as well:
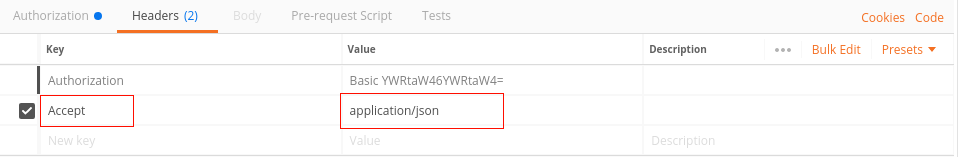
The request is now ready, and can be sent by clicking on the Send button.
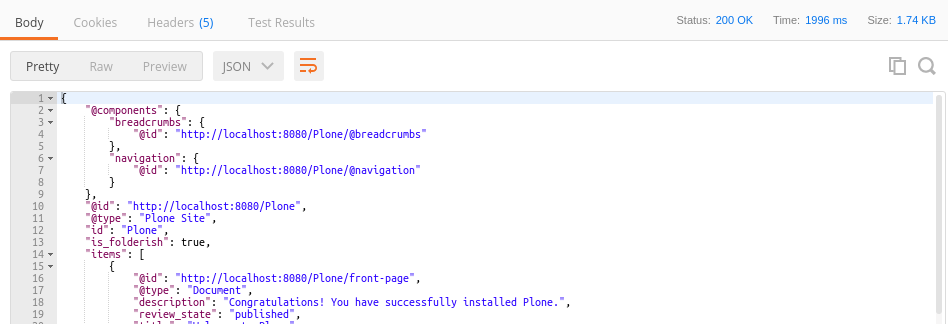
The Response of the server is now displayed below the Request.
You can follow the links on the @id attributes by clicking on them.
For every link Postman has prepared, another request sharing the same headers can be sent again by clicking on the Send button.
Conclusion
You can now explore the whole stucture of your application easily via the API using GET requests.